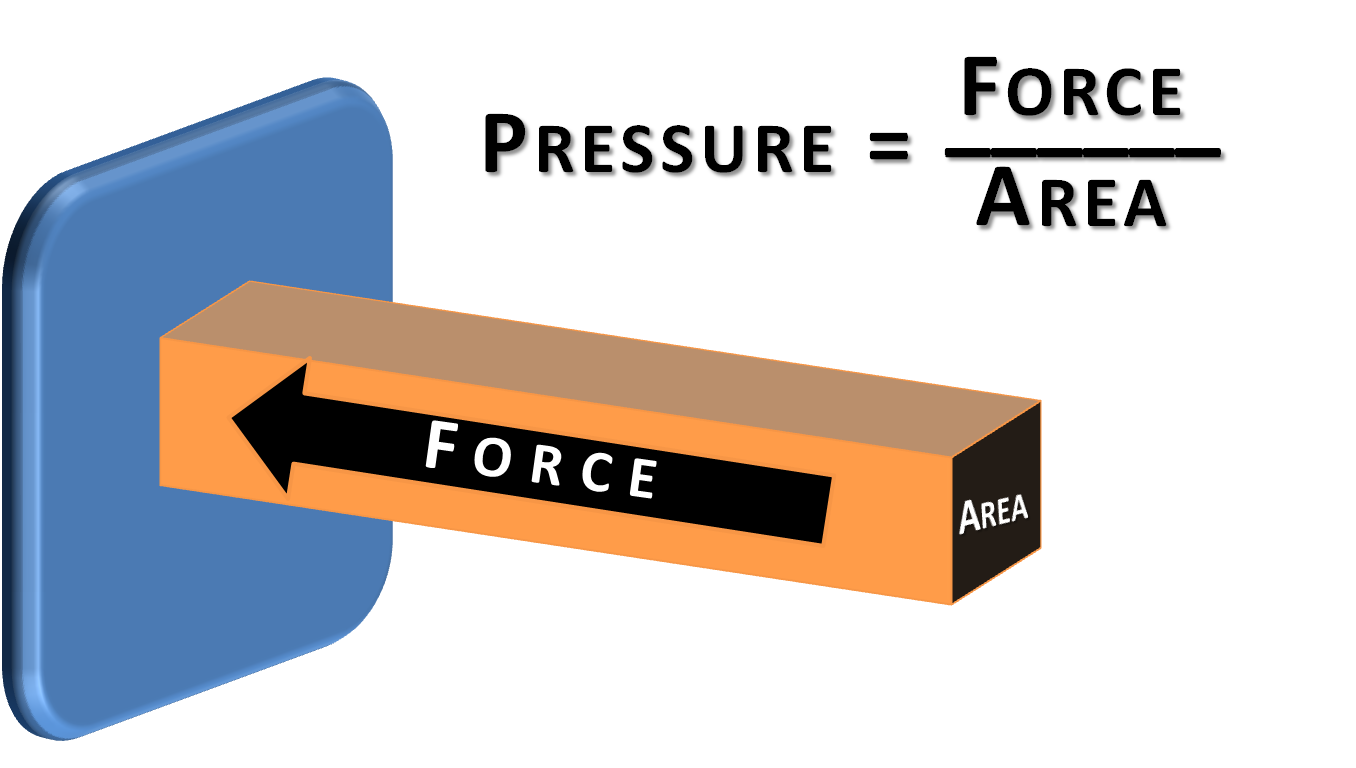
Pressure: Pressure is defined as force acting normally on unit area of the surface. Pressure (P)= F/A SI unit of pressure is N / m2 also called pascal (Pa). Pressure is a scalar quantity.
Atmospheric Pressure: Atmospheric pressure is that pressure which is exerted by a mercury column of 76 cm length at 0°C at 450 latitude at the sea-level. It is equal to weight of 76 cm column of mercury of cross-sectional area 1 cm2. Generally it is measured in bar. 1 bar = 105 N/m2 Atmospheric pressure 1 atm = 1.01 bar = 1.01 x 105 N/m2 = 760 torr One torr is the pressure exerted by a mercury column of 1 mm length.
>> Atmospheric pressure decreases with altitude (height from earth’s surface).
This is why 1. It is difficult to cook on the mountain 2. The fountain pen of a passenger leaks in airplane at height.
>> Atmospheric pressure is measured by barometer. With the help of barometer, weather forecast can be made.
- Sudden fall in barometric reading is the indication of storm.
- Slow fall in barometric reading is the indication of rain.
- Slow rise in the barometric reading is the indication of clear weather.
Pressure in liquid: Force exerted on unit area of wall or base of the container by the molecules of liquid is the pressure of liquid.
The pressure exerted by liquid at depth h below the surface of liquid is given as p = hdg where d is the density of liquid.
>> Regarding pressure, the following points are worth noting :
1. In a static liquid at same horizontal level, pressure is same at all points. 2. Pressure at a point in a static liquid has same value in all directions. 3. Pressure at a point in a liquid is proportional to the depth of the point from the free surface. 4. Pressure at a point in a liquid is proportional to the density of the liquid.
Pascal law for pressure of liquid
1. If gravitational attraction is negligible, in equilibrium condition, pressure is same at all points in a liquid.
2. If an external pressure is applied to an exclosed fluid, it is transmitted undiminished to every direction.
>> Hydrolic lift, hydrolic press, Hydrolic brake work on Pascal law.
Effect of pressure on Melting Point and Boiling Point
- The M.P. of substances which expands on fusion increases with the increase in pressure; for example – wax.
- The M.P. of substances which contracts on fusion decreases with the increase in temperature; for example – ice.
- Boiling point of all the substances increases with the increase in pressure.
Floatation
Buoyant Force: When a body is immersed partly or wholly in a liquid, a force acts on the body by the liquid in the upward direction. This force is called Buoyant force or force of buoyancy or upthrust. It is equal to the weight of liquid displaced by the body and acts at the centre of gravity of displaced liquid. Its study was first made by Archimedes.
Archimedes Principle: When a body is immersed partly or wholly in a liquid, there is an apparent loss in the weight of the body which is equal to the weight of liquid displaced by the body.
Law of Floatation
A body floats in a liquid if
- Density of material of body is less than or equal to the density of liquid.
- If density of material of body is equal to density of liquid, the body floats fully submerged in liquid in neutral equilibrium.
- When body floats in neutral equilibrium, the weight of the body is equal to the weight of displaced liquid.
- The centre of gravity of the body and centre of gravity of the displaced liquid should be in one vertical line.
Centre of Buoyancy: The centre of gravity of the liquid displaced by a body is called centre of buoyancy.
Meta Centre: When a floating body is slightly tilted from equilibrium position, the centre of buoyancy shifts. The point at which the vertical line passing through the new position of centre of buoyancy meets with the initial line is called meta centre.
Density: Density is defined as mass per unit volume. Density = mass/ volume. Its SI unit is kg/m3.
Relative density = density of material/ density of water at 4°C Since relative density is a ratio, it is unitless.
>> Relative density is measured by Hydrometer.
>> The density of sea water is more than that of normal water. This explains why it is easier to swim in sea water.
>> When ice floats in water, its 1/10 the part remain outside the water.
>> If ice floating in water in a vessel melts, the level of water in the vessel does not change.
>> Purity of milk is measured by lactometer.